Author: Ir. Dr. Justin LAI Woon Fatt | 30th January 2025
INTRODUCTION
The Malaysian government has approved amendments to the Uniform Building By-Law (UBBL) 1984 through the 78th National Council for Local Government (MNKT) on 13 July 2021 [1]. One of the revised items is By-law 5, which mandates that construction projects must be overseen full-time by a Construction Project Manager and Site Construction Supervisor certified by Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB). Furthermore, this Amendment also approves that the Form G submitted to obtain Certificate of Completion and Compliance (CCC) must be certified by a Construction Project Manager recognised by CIDB. In addition, CIDB has partnered with the Local Government Department (JKT), the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM), and the Board of Architects Malaysia (LAM) to determine the qualifications of Construction Project Managers, ensuring that this amendment can be executed effectively without affecting industry stakeholders.
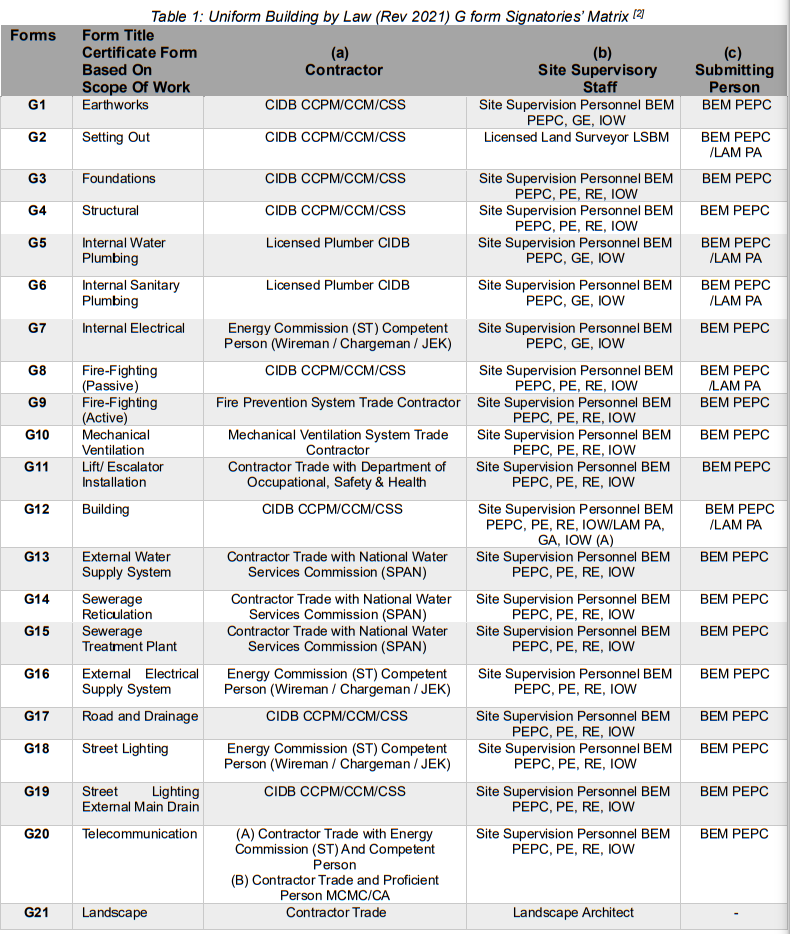
G FORM SIGNATURES’ MATRIX
The signature matrix for Form G can be referenced by the responsible parties during the certification stage, prior to obtaining the CCC.
Figure 1: Form G1 Earthworks Certification [By-law 25 or 27] Amendment 2021 [3]
ELIGIBILITY OF CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGER
Confusion often arises regarding when a Certified Construction Manager (CCM) and Certified Construction Project Manager (CCPM) should sign Form G, as well as the project criteria that require CCM or CCPM’s signatures. CIDB has addressed this by issuing a statement outlining the necessary qualifications for Construction Project Manager, as detailed in Table 2.
A registered Construction Project Manager (CPM) with CIDB (Construction Industry Development Board) typically refers to an individual who has met the necessary requirements set by CIDB to be officially recognized as a qualified manager for construction projects. The Certified Construction Project Manager (CCPM) program and Certified Construction Manager (CCM) program are implemented in three assessment modes, such as Mode I(a) – Training & Assessment, Mode I(b) – Assessment only, and Mode II (RPLE) – which is Recognition Through Level of Education and Experience (Recognition Prior Learning and Experience, RPLE) [5][6]. Successful candidates having passed through any mode will be accredited with a Level 5 Construction Skills Competency Certificate (CSCC) for Certified Construction Manager (CCM), while CCPM candidates will be accredited with a Level 6 Construction Skills Competency Certificate (CSCC).
The definitions used to explain the meaning of Construction Project Manager and Construction Site Supervisor are as follows:
A Certified Construction Project Manager (CCPM) is a professional accredited by the CIDB, demonstrating extensive knowledge and competence in managing construction projects. The CCPM is responsible for planning, coordinating, organizing, monitoring, controlling, mitigating, and handing over construction projects, ensuring they meet the expected cost, duration, and quality standards throughout the project lifecycle. In addition to technical expertise, the CCPM upholds professional ethics and fosters a culture of environmental sustainability, safety, and health in the workplace. This role involves effective communication, leadership, and motivation of project teams and stakeholders to achieve project objectives successfully.
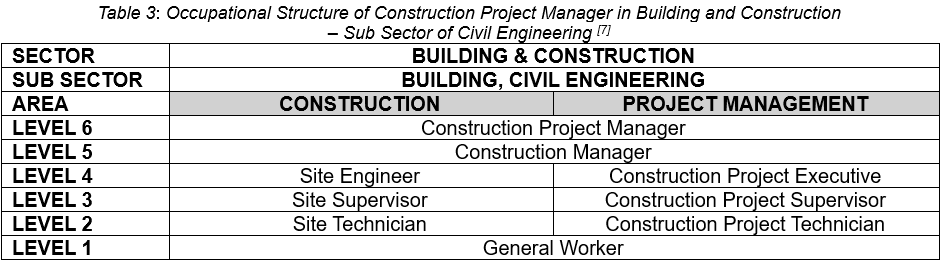
The occupational structure for the Construction Project Manager in the Building and Construction is highlighted in Table 3.
A Certified Construction Manager (CCM) plays a pivotal role in leading the construction implementation process at the project site. In carrying out these responsibilities, the CCM must maintain productivity to meet project objectives, effectively communicate project processes, ensuring that all team members and stakeholders clearly understand their roles, responsibilities, and project expectations. This includes addressing on-site challenges, resolving conflicts, mitigating risks, and ensuring compliance with safety, quality, and regulatory standards.
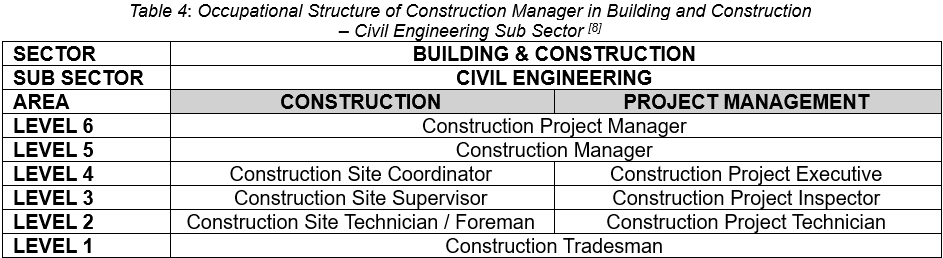
The occupational structure for the Construction Manager in the Building and Construction is highlighted in Table 4.
Table 3 and Table 4 outlines the hierarchical structure of occupational areas of construction project management within the building and construction sector specifically focusing on the sub-sector of civil engineering. The ‘’sector’’ refers to the broader industry, while the ‘’sub-sector’’ narrows it down to a specific area – in this case, civil engineering.
The levels, ranging from 1 to 6, define a progression or hierarchy of roles and responsibilities within the construction project management area. Overall, the structure represents the usual career path for someone in construction project management within the civil engineering field. It starts with beginner roles and moves up to positions with more responsibility and leadership.
A Construction Site Supervisor (CSS) is a professional responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations on a construction site. They ensure that construction projects are completed safely, on time, and according to plans and specifications. Their duties typically include managing workers, coordinating activities, monitoring progress, ensuring compliance with safety regulations, and resolving issues that arise during construction [9].
CONCLUSION
In summary, it’s crucial for all construction stakeholders to adhere to the amendments concerning the qualifications required for the Construction Project Manager authorized to sign Form G, as per the Uniform Building By-Law (UBBL) 1994 (amendment 2021). Non-compliance with these criteria may result in the rejection of their CCC application by the local authority. Therefore, staying informed about the latest regulatory updates and ensuring ongoing compliance is essential for the successful execution of construction projects and maintaining a positive reputation within the industry.
**The amended UBBL has yet to be gazetted by the respective state governments.
Ir. Dr. Justin LAI Woon Fatt
CEO/ Founder
IPM Group
References:
[1] Construction Personnel Malaysia (2023). CIDB Official Letter Regarding UBBL 1984. Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.construction.org.my/2023/06/07/cidb-official-letter-regarding-ubbl-1984/
[2] Construction Personnel Malaysia (n.d.). Uniform Building by Law (Rev 2021) G Form Signatories Matrix. Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.construction.org.my/ubbl-g-form-signatories-matrix/
[3] Government of Malaysia. (2022). Street, Drainage and Building Act 1974 (Act 133). G.N. 5178/84. Uniform Building By-Laws 1984. Amendment 2021. Jabatan Kerajaan Tempatan, Kementerian Perumahan dan Kerajaan Tempatan. Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://jkkp-fktm.unimap.edu.my/images/Analisis_APA/Undang2/UKBS_1984.pdf
[4] Construction Industry Development Board Malaysia. (2023). Determination of Eligibility of Construction Project Manager Who Signs the Form G Based on Uniform Building By-Laws (UBBL) 1984 (Amendment 2021).1 CIDB Circular No. 3/2023. 30th January 2025 https://mbam.org.my/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/27032023-TRANSLATION-OF-CIDB-Circular-No.3.2023.pdf
[5] Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB) Malaysia (2024). Certified Construction Project Manager (CCPM). 30th January 2025 from https://www.cidb.gov.my/eng/certified-construction-project-manager-ccpm/
[6] Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB) Malaysia (2024). Certified Construction Manager (CCM). Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.cidb.gov.my/eng/certified-construction-manager-ccm/
[7] Construction Industry Development Board Malaysia. (n.d.). Construction Industry Competency Standard (CICS) for Certified Construction Project Managers (CCPM) in Malaysia. Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.cidb.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/CCPM-CICS-LEVEL-6-CIDB.pdf
[8] Construction Industry Development Board Malaysia. (n.d.). Construction Industry Competency Standard (CICS) for Certified Construction Managers (CCM) in Malaysia. Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.cidb.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/CCM-CICS-CIDB-BPP.pdf
[9] Construction Industry Development Board Malaysia. (n.d). Certified Construction Site Supervisor (CSS). Retrieved on 30th January 2025 from https://www.cidb.gov.my/eng/certified-construction-site-supervisor-css/